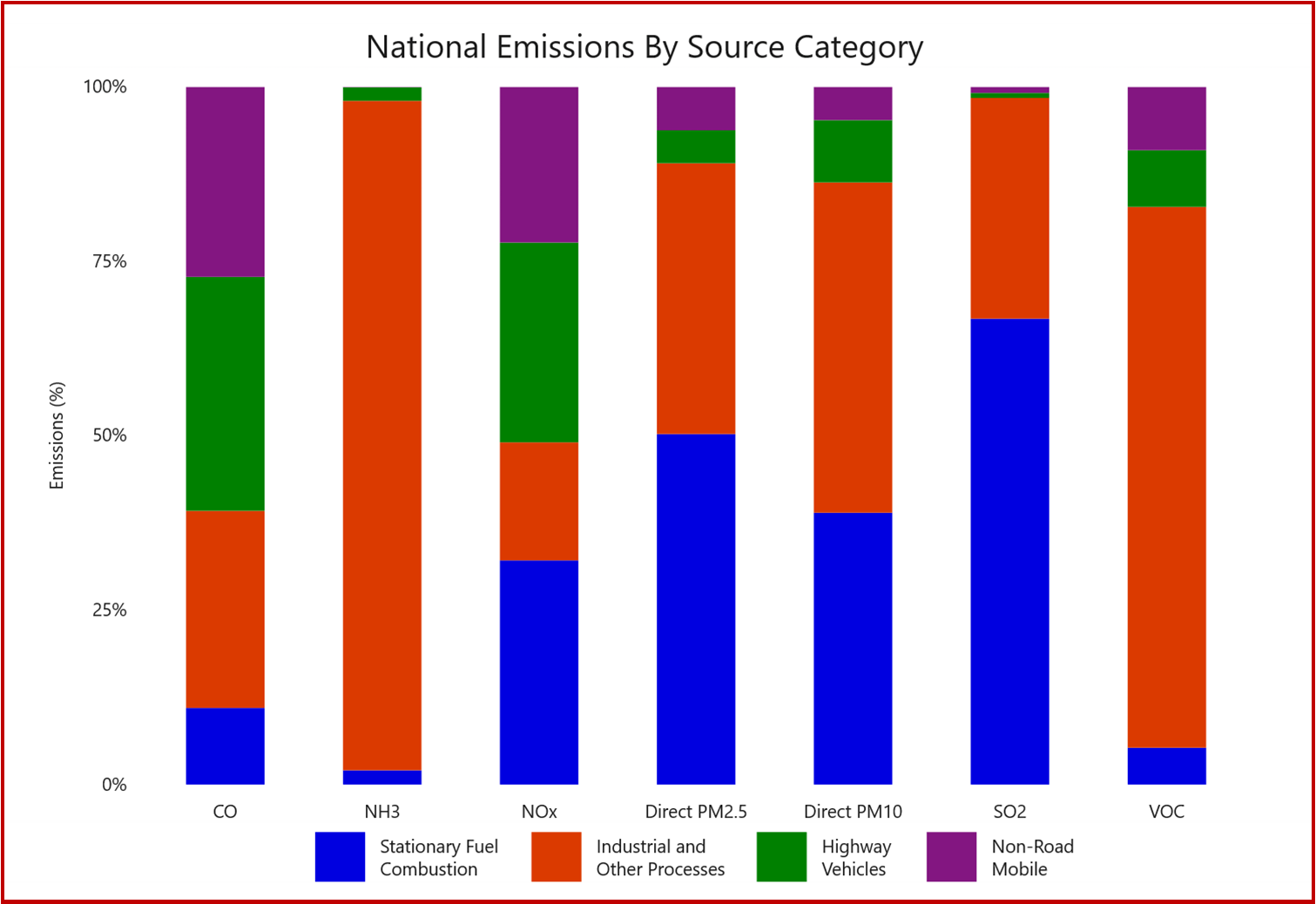
Click for more information.
Emissions of air pollution come from:
• stationary fuel combustion sources (such as electric utilities and industrial boilers),
• industrial and other processes (such as metal smelters, petroleum refineries, cement kilns and dry cleaners),
• highway vehicles, and
• non-road mobile sources (such as recreational and construction equipment, marine vessels, aircraft and locomotives).
Air pollution contains gas and particle contaminants that are present in the atmosphere. Gaseous pollutants include sulfur dioxide (SO2), oxides of nitrogen (NOx), ozone (O3), carbon monoxide (CO), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and certain toxic air pollutants. Particle pollution (PM2.5 and PM10) includes a mixture of compounds that EPA groups into five major categories: sulfate, nitrate, elemental (black) carbon, organic carbon and crustal material.