
Researchers found that switching an internal-combustion-engine vehicle to a BEV results in greater total tonnage of emissions reductions as the vehicle size increases, due to the greater fuel consumption of larger vehicles.
University of Michigan and Ford Motor Company researchers in a new study that evaluated the savings in greenhouse gas emissions between electric and gasoline-powered vehicles say light-duty, battery-electric vehicles have ~64% lower cradle-to-grave life cycle greenhouse gas emissions than internal-combustion-engine vehicles on average across the United States.
“This is an important study to inform and encourage climate action. Our research clearly shows substantial greenhouse gas emission reductions that can be achieved from transitioning to electrified powertrains across all vehicle classes,” said study senior author Greg Keoleian, a professor at the U-M School for Environment and Sustainability and director of the U-M Center for Sustainable Systems.
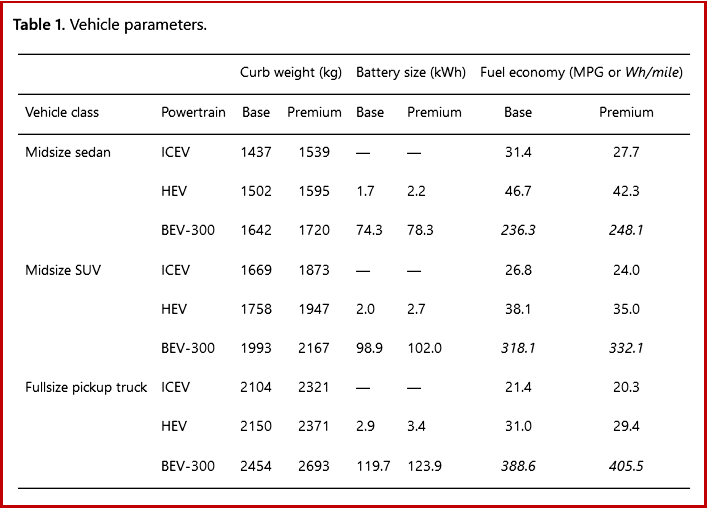 Researchers looked at three different model year 2020 powertrain options—internal-combustion-engine vehicles, hybrid-electric vehicles, and battery-electric vehicles – for midsize sedans, midsize SUVs, and full-size pickup trucks, accounting for differences in fuel economy, annual mileage, vehicle production, and vehicle lifetime across vehicle classes. In the study, researchers also conducted a cradle-to-grave life cycle assessment of pickup trucks and compared the implications of pickup truck electrification to those of sedan and SUV electrification.
Researchers looked at three different model year 2020 powertrain options—internal-combustion-engine vehicles, hybrid-electric vehicles, and battery-electric vehicles – for midsize sedans, midsize SUVs, and full-size pickup trucks, accounting for differences in fuel economy, annual mileage, vehicle production, and vehicle lifetime across vehicle classes. In the study, researchers also conducted a cradle-to-grave life cycle assessment of pickup trucks and compared the implications of pickup truck electrification to those of sedan and SUV electrification.
Researchers found that switching an internal-combustion-engine vehicle to a BEV results in greater total tonnage of emissions reductions as the vehicle size increases, due to the greater fuel consumption of larger vehicles.
“Though the percentage savings is approximately the same across vehicle classes, on average replacing an internal-combustion-engine sedan with a battery-electric sedan saves 45 metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent, replacing an internal-combustion-engine SUV with a battery-electric SUV saves 56 metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent, and replacing an internal-combustion-engine pickup with a battery-electric pickup saves 74 metric tons carbon dioxide equivalent over the lifetime of the vehicles,” said study first author and Center for Sustainable Systems Research Specialist Max Woody. This appears to be conforming the obvious as pickup truck fuel consumption and hours of use and lifetime tend to be greater than other vehicles.
The researchers also found that BEVs have larger greenhouse gas emissions in their manufacturing than internal-combustion-engine vehicles, due to battery production. However, this impact is offset by savings in their operation. For battery-electric vehicles and internal-combustion-engine vehicles, the breakeven time is 1.2 to 1.3 years for sedans, 1.4 to 1.6 years for SUVs, and 1.3 years for pickup trucks, based on the average U.S. grid and vehicle miles traveled.
Vehicle emissions vary across the country, as different temperatures and different drive cycles affect a vehicle’s fuel economy. For electric vehicles, the emissions intensity of the local electricity grid is also an important factor. The study developed maps to show the lifetime grams of carbon dioxide equivalent/mile for each powertrain (internal-combustion-engine vehicles, hybrid vehicles, and battery-electric vehicles) and vehicle type (sedan, SUV, and pickup truck) by county across the United States.
Researchers found that concerns about battery-electric vehicles having higher emissions than internal-combustion-engine vehicles or hybrids are largely unfounded, as BEVs outperform hybrids in 95% to 96% of counties, while BEVs outperform internal-combustion-engine vehicles in 98% to 99% of counties, even assuming only modest progress towards grid de-carbonization.
Charging strategies can further reduce battery-electric vehicle greenhouse gas emissions. The study found that charging during the hours of the day with the lowest grid emissions intensity can reduce emissions by 11% on average. “Deployment of electric vehicles and expansion of renewable energy resources like solar and wind should be done at the same time; the benefit of each is increased by the development of the other,” said Woody.
The study, “The role of pickup truck electrification in the de-carbonization of light-duty vehicles,” was published online March 1 in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
The other authors of the study are Parth Vaishnav of the U-M School for Environment and Sustainability and Center for Sustainable Systems and Robert De Kleine, Hyung Chul Kim, James E. Anderson, and Timothy J. Wallington of Ford Motor Company’s Research and Innovation Center. This study was supported by Ford Motor Company through a Ford-University of Michigan Alliance Project Award.

About Ken Zino
Ken Zino, editor and publisher of AutoInformed, is a versatile auto industry participant with global experience spanning decades in print and broadcast journalism, as well as social media. He has automobile testing, marketing, public relations and communications experience. He is past president of The International Motor Press Assn, the Detroit Press Club, founding member and first President of the Automotive Press Assn. He is a member of APA, IMPA and the Midwest Automotive Press Assn.
He also brings an historical perspective while citing their contemporary relevance of the work of legendary auto writers such as Ken Purdy, Jim Dunne or Jerry Flint, or writers such as Red Smith, Mark Twain, Thomas Jefferson – all to bring perspective to a chaotic automotive universe.
Above all, decades after he first drove a car, Zino still revels in the sound of the exhaust as the throttle is blipped during a downshift and the driver’s rush that occurs when the entry, apex and exit points of a turn are smoothly and swiftly crossed. It’s the beginning of a perfect lap.
AutoInformed has an editorial philosophy that loves transportation machines of all kinds while promoting critical thinking about the future use of cars and trucks.
Zino builds AutoInformed from his background in automotive journalism starting at Hearst Publishing in New York City on Motor and MotorTech Magazines and car testing where he reviewed hundreds of vehicles in his decade-long stint as the Detroit Bureau Chief of Road & Track magazine. Zino has also worked in Europe, and Asia – now the largest automotive market in the world with China at its center.


University of Michigan, Ford – EV Greenhouse Gas Reductions Greater than Others. Pickups Best Over Their Life Cycle?
Researchers found that switching an internal-combustion-engine vehicle to a BEV results in greater total tonnage of emissions reductions as the vehicle size increases, due to the greater fuel consumption of larger vehicles.
University of Michigan and Ford Motor Company researchers in a new study that evaluated the savings in greenhouse gas emissions between electric and gasoline-powered vehicles say light-duty, battery-electric vehicles have ~64% lower cradle-to-grave life cycle greenhouse gas emissions than internal-combustion-engine vehicles on average across the United States.
“This is an important study to inform and encourage climate action. Our research clearly shows substantial greenhouse gas emission reductions that can be achieved from transitioning to electrified powertrains across all vehicle classes,” said study senior author Greg Keoleian, a professor at the U-M School for Environment and Sustainability and director of the U-M Center for Sustainable Systems.
Researchers found that switching an internal-combustion-engine vehicle to a BEV results in greater total tonnage of emissions reductions as the vehicle size increases, due to the greater fuel consumption of larger vehicles.
“Though the percentage savings is approximately the same across vehicle classes, on average replacing an internal-combustion-engine sedan with a battery-electric sedan saves 45 metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent, replacing an internal-combustion-engine SUV with a battery-electric SUV saves 56 metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent, and replacing an internal-combustion-engine pickup with a battery-electric pickup saves 74 metric tons carbon dioxide equivalent over the lifetime of the vehicles,” said study first author and Center for Sustainable Systems Research Specialist Max Woody. This appears to be conforming the obvious as pickup truck fuel consumption and hours of use and lifetime tend to be greater than other vehicles.
The researchers also found that BEVs have larger greenhouse gas emissions in their manufacturing than internal-combustion-engine vehicles, due to battery production. However, this impact is offset by savings in their operation. For battery-electric vehicles and internal-combustion-engine vehicles, the breakeven time is 1.2 to 1.3 years for sedans, 1.4 to 1.6 years for SUVs, and 1.3 years for pickup trucks, based on the average U.S. grid and vehicle miles traveled.
Vehicle emissions vary across the country, as different temperatures and different drive cycles affect a vehicle’s fuel economy. For electric vehicles, the emissions intensity of the local electricity grid is also an important factor. The study developed maps to show the lifetime grams of carbon dioxide equivalent/mile for each powertrain (internal-combustion-engine vehicles, hybrid vehicles, and battery-electric vehicles) and vehicle type (sedan, SUV, and pickup truck) by county across the United States.
Researchers found that concerns about battery-electric vehicles having higher emissions than internal-combustion-engine vehicles or hybrids are largely unfounded, as BEVs outperform hybrids in 95% to 96% of counties, while BEVs outperform internal-combustion-engine vehicles in 98% to 99% of counties, even assuming only modest progress towards grid de-carbonization.
Charging strategies can further reduce battery-electric vehicle greenhouse gas emissions. The study found that charging during the hours of the day with the lowest grid emissions intensity can reduce emissions by 11% on average. “Deployment of electric vehicles and expansion of renewable energy resources like solar and wind should be done at the same time; the benefit of each is increased by the development of the other,” said Woody.
The study, “The role of pickup truck electrification in the de-carbonization of light-duty vehicles,” was published online March 1 in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
The other authors of the study are Parth Vaishnav of the U-M School for Environment and Sustainability and Center for Sustainable Systems and Robert De Kleine, Hyung Chul Kim, James E. Anderson, and Timothy J. Wallington of Ford Motor Company’s Research and Innovation Center. This study was supported by Ford Motor Company through a Ford-University of Michigan Alliance Project Award.
About Ken Zino
Ken Zino, editor and publisher of AutoInformed, is a versatile auto industry participant with global experience spanning decades in print and broadcast journalism, as well as social media. He has automobile testing, marketing, public relations and communications experience. He is past president of The International Motor Press Assn, the Detroit Press Club, founding member and first President of the Automotive Press Assn. He is a member of APA, IMPA and the Midwest Automotive Press Assn. He also brings an historical perspective while citing their contemporary relevance of the work of legendary auto writers such as Ken Purdy, Jim Dunne or Jerry Flint, or writers such as Red Smith, Mark Twain, Thomas Jefferson – all to bring perspective to a chaotic automotive universe. Above all, decades after he first drove a car, Zino still revels in the sound of the exhaust as the throttle is blipped during a downshift and the driver’s rush that occurs when the entry, apex and exit points of a turn are smoothly and swiftly crossed. It’s the beginning of a perfect lap. AutoInformed has an editorial philosophy that loves transportation machines of all kinds while promoting critical thinking about the future use of cars and trucks. Zino builds AutoInformed from his background in automotive journalism starting at Hearst Publishing in New York City on Motor and MotorTech Magazines and car testing where he reviewed hundreds of vehicles in his decade-long stint as the Detroit Bureau Chief of Road & Track magazine. Zino has also worked in Europe, and Asia – now the largest automotive market in the world with China at its center.