Hyundai Motor Group has announced the development of what it claims reduces noise within the cabin of a vehicle. RANC builds on the Group’s current Active Noise Control (ANC) technology, which reduces noise by emitting soundwaves inverted to incoming noise thereby cancelling each other out. ANC is a well-known technology that analyses inside cabin sound to decrease engine and road noise, versus the older passive method of blocking noise through sound insulation.
There is almost no powertrain noise from electric and fuel cell electric vehicles, so mitigating road and wind noise becomes more vital. Using RANC can significantly reduce road noise and create a serene cabin for future electric and fuel cell electric vehicles. The technology will begin to be applied to an upcoming Genesis model.
The existing noise insulation method involved sound insulations and dynamic dampers, increased weight but couldn’t block the buzzing infrasound completely. In contrast, ANC uses lighter parts – microphones and controllers – to limit the noise and reduces infrasound more efficiently. The technology is already available in some vehicles.
Due to limitations of noise measurement and analysis technology, the existing ANC was only able to be used when noise was constant and the occurrence of the noise predictable. The Group’s current ANC technology has been most commonly used to counteract constant engine noise. Since it only takes about 0.009 second for road or engine noise to reach the passenger, the current technology was constrained.
With RANC technology, Hyundai is able to considerably improve in-cabin quietness. The new system can analyze various types of noise in real-time and produce cancelling inverted soundwaves. There are different types of road noises that the new technology can process, such as resonant sounds created between tires and wheels or rumble sounds coming from the road.
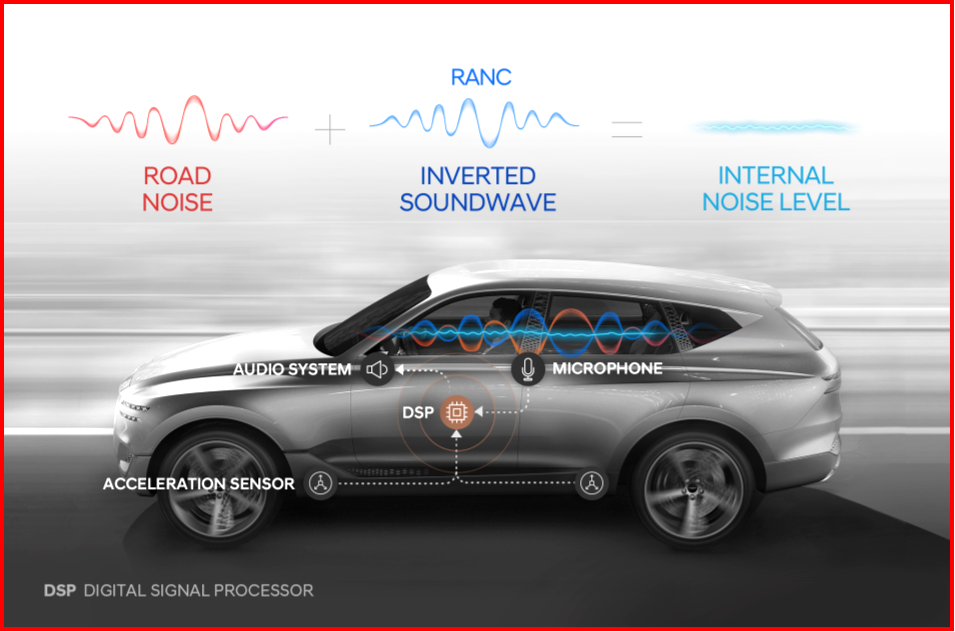
The working principle of RANC uses an acceleration sensor and calculates the vibration from the road to the car and the control computer analyzes road noise. It only takes 0.002 second to analyze the noise and produce an inverted sound-wave, generated by the DSP (Digital Signal Processor). The microphone constantly monitors the road noise cancellation status and sends the information to the DSP. RANC is able to conduct accurate noise analysis and rapid computation to combat road noise for the driver’s seat, the passenger seat and rear seats separately.
Based on tests evaluating road surface, vehicle speed, and different seating positions, RANC was able to reduce in-cabin noise by 3dB. That 3dB level is roughly half the noise level as compared without RANC. With this achievement, the Group can potentially decrease the amount of unsprung weight in a vehicle with fewer sound-insulating parts and dampers compared with before.
Cabin quietness becomes more important as internal combustion vehicles are phased out. Vehicle interior noise primarily comes from three sources:
- Vehicle powertrain noise,
- Road noise, and
- Wind noise.


Pingback: Genesis Launches Its First SUV – GV80 | AutoInformed