Putin’s war will make things worse…
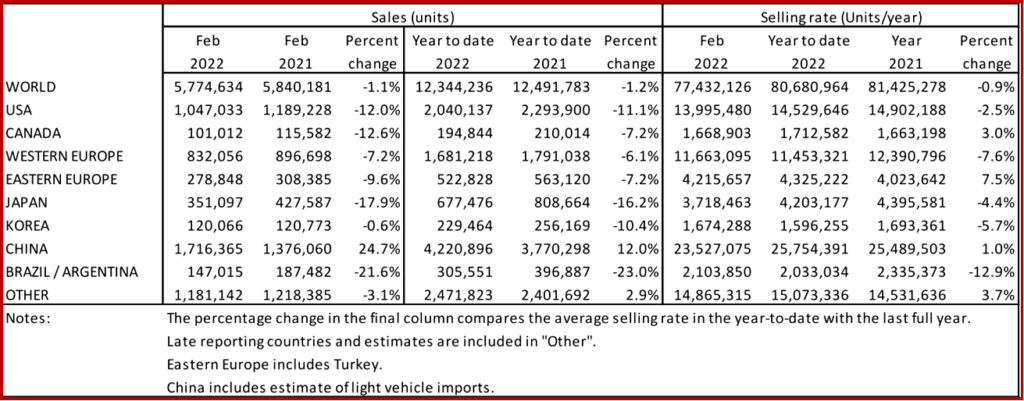
The Global Light Vehicle (LV) selling rate dropped to 77 million units annually in February 2022, according to consultancy LMC. Even with the disruption to the world’s largest auto market due to the Chinese New Year, sales for the rest of the globe were weaker compared with the month before. Year-on-year (YoY) sales were 1% down on a poor base performance last February.
“Sales continue to be held back by supply-side issues, though underlying demand is also being eroded as the economic outlook deteriorates,” said LMC. Following are LMC observations by market.
US Light Vehicle sales fell by 12.0% YoY in February, to 1.05 million units. The selling rate declined to 14.0 million units/year, from 15.1 million units/year in January. However, this measure can be misleading at present, since supply, rather than demand, is driving sales and disrupting normal seasonality. Average transaction prices eased slightly in February, to $44,132, but were still up by 17.6% YoY. Incentives continued to head lower last month, to $1,245 average per vehicle. There was a slight recovery in fleet sales in February, but they remain well below pre-pandemic levels.
Indeed, yesterday at an International Motor Press Association meeting I attended, a Hyundai product planner noted that they didn’t even know how many Ioniq5 models they were getting next week, let alone have a sales projection for the year. (AutoInformed: Hyundai Revises Ioniq EV for 2022 with New Platform)
In Canada, LV sales declined by 12.6% YoY in February to 101,000 units. The selling rate slowed to 1.67 million units/year in February, from 1.76 million units/year in January. However, “there has been very little change over recent months as the market continues to battle against low inventory.,” LMC said.
In Mexico, sales were down by 3.4% YoY in February, to 79,000 units, while the selling rate picked up to 1.06 million units/year, from 1.01 million units/year in January, nominally the strongest since June 2021.
The West European selling rate increased only slightly to 11.7 million units/year in February, from 11.2 million units/year in January. Last month’s result reflects the fact that supply constraints faced by the automotive industry remain a significant “headwind” to sales volumes.
The East European selling rate was 4.2 million units/year last month, which was a “disappointing fall from January’s 4.4 million units/year as familiar supply issues disrupted performance. The evolving Russia-Ukraine conflict, and related sanctions, will clearly hit regional selling rates as the year progresses.,” LMC said.
China: According to preliminary data in the opaque communist market, the selling rate in China decelerated sharply in February, even after it was adjusted for the Chinese New Year holiday. The February selling rate was 23.5 million units/year, down 16% from a robust January. In the first two months of this year, the selling rate averaged 25.8 million units/year, slightly above last year’s total Light Vehicle sales of 25.5 million units. In YoY terms, however, sales (wholesales) expanded by 25% in February and 12% YTD, due to low bases in the calculation.
Sales of Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs) slowed faster than those of Passenger Vehicles (PVs), as replacement demand for LCVs weakened after the implementation of the stricter emission standards in 2020 and 2021. PV sales remained relatively resilient, as the chip shortage continued to ease and OEMs ramped up production. New Electric Vehicle sales increased by 182% YoY in February, despite the 30% reduction in the government subsidies for 2022, and the rising cost of batteries.
The Japanese market decelerated sharply in February, disrupted by skyrocketing Omicron infections and supply shortages of new vehicles. Rising inflation (in a country that is known for decades of deflationary trend) also dampened consumer confidence and spending. The February selling rate was 3.7 million units/year, down 21% from a robust January. In YoY terms, sales declined by 18% in February (the eighth consecutive month of contraction).
After a weak start to the New Year, sales in Korea accelerated in February. The February selling rate was 1.67 million units/year, up 10% from a weak January. The improvement in sales was expected, as a slump in January was caused mainly by the temporary shutdown of Hyundai’s Asan plant to upgrade the facility for production of the IONIQ 6 BEV. The easing of supply issues, including the chip shortage, also helped production and sales. In YoY terms, however, sales declined marginally due to a high-base effect.
Brazilian LV sales fell by 24.3% YoY in February, to 120,000 units. The selling rate increased to 1.75 million units/year in February, from 1.63 million units/year in January, but only in one month in 2021 was the selling rate lower than it was in February. In addition to supply-side issues, demand now appears to be waning as a result of declining affordability. A weak Real (BRL) is exacerbating inflation, and interest rates have been hiked sharply – and repeatedly – in an attempt to combat rising prices.
In Argentina, LV sales were down by 6.3% YoY in February, to 27,000 units. The selling rate increased to 350,000 units/year, up from 336,000 units/year in January. High inflation, rising interest rates (as required by an agreement with the International Monetary Fund), import restrictions, and chip-related inventory shortages are all contributing to the sluggish state of the market.

About Ken Zino
Ken Zino, editor and publisher of AutoInformed, is a versatile auto industry participant with global experience spanning decades in print and broadcast journalism, as well as social media. He has automobile testing, marketing, public relations and communications experience. He is past president of The International Motor Press Assn, the Detroit Press Club, founding member and first President of the Automotive Press Assn. He is a member of APA, IMPA and the Midwest Automotive Press Assn.
He also brings an historical perspective while citing their contemporary relevance of the work of legendary auto writers such as Ken Purdy, Jim Dunne or Jerry Flint, or writers such as Red Smith, Mark Twain, Thomas Jefferson – all to bring perspective to a chaotic automotive universe.
Above all, decades after he first drove a car, Zino still revels in the sound of the exhaust as the throttle is blipped during a downshift and the driver’s rush that occurs when the entry, apex and exit points of a turn are smoothly and swiftly crossed. It’s the beginning of a perfect lap.
AutoInformed has an editorial philosophy that loves transportation machines of all kinds while promoting critical thinking about the future use of cars and trucks.
Zino builds AutoInformed from his background in automotive journalism starting at Hearst Publishing in New York City on Motor and MotorTech Magazines and car testing where he reviewed hundreds of vehicles in his decade-long stint as the Detroit Bureau Chief of Road & Track magazine. Zino has also worked in Europe, and Asia – now the largest automotive market in the world with China at its center.


Global Light Vehicle Sales Rate Drops in February
Putin’s war will make things worse…
The Global Light Vehicle (LV) selling rate dropped to 77 million units annually in February 2022, according to consultancy LMC. Even with the disruption to the world’s largest auto market due to the Chinese New Year, sales for the rest of the globe were weaker compared with the month before. Year-on-year (YoY) sales were 1% down on a poor base performance last February.
“Sales continue to be held back by supply-side issues, though underlying demand is also being eroded as the economic outlook deteriorates,” said LMC. Following are LMC observations by market.
US Light Vehicle sales fell by 12.0% YoY in February, to 1.05 million units. The selling rate declined to 14.0 million units/year, from 15.1 million units/year in January. However, this measure can be misleading at present, since supply, rather than demand, is driving sales and disrupting normal seasonality. Average transaction prices eased slightly in February, to $44,132, but were still up by 17.6% YoY. Incentives continued to head lower last month, to $1,245 average per vehicle. There was a slight recovery in fleet sales in February, but they remain well below pre-pandemic levels.
Indeed, yesterday at an International Motor Press Association meeting I attended, a Hyundai product planner noted that they didn’t even know how many Ioniq5 models they were getting next week, let alone have a sales projection for the year. (AutoInformed: Hyundai Revises Ioniq EV for 2022 with New Platform)
In Canada, LV sales declined by 12.6% YoY in February to 101,000 units. The selling rate slowed to 1.67 million units/year in February, from 1.76 million units/year in January. However, “there has been very little change over recent months as the market continues to battle against low inventory.,” LMC said.
In Mexico, sales were down by 3.4% YoY in February, to 79,000 units, while the selling rate picked up to 1.06 million units/year, from 1.01 million units/year in January, nominally the strongest since June 2021.
The West European selling rate increased only slightly to 11.7 million units/year in February, from 11.2 million units/year in January. Last month’s result reflects the fact that supply constraints faced by the automotive industry remain a significant “headwind” to sales volumes.
The East European selling rate was 4.2 million units/year last month, which was a “disappointing fall from January’s 4.4 million units/year as familiar supply issues disrupted performance. The evolving Russia-Ukraine conflict, and related sanctions, will clearly hit regional selling rates as the year progresses.,” LMC said.
China: According to preliminary data in the opaque communist market, the selling rate in China decelerated sharply in February, even after it was adjusted for the Chinese New Year holiday. The February selling rate was 23.5 million units/year, down 16% from a robust January. In the first two months of this year, the selling rate averaged 25.8 million units/year, slightly above last year’s total Light Vehicle sales of 25.5 million units. In YoY terms, however, sales (wholesales) expanded by 25% in February and 12% YTD, due to low bases in the calculation.
Sales of Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs) slowed faster than those of Passenger Vehicles (PVs), as replacement demand for LCVs weakened after the implementation of the stricter emission standards in 2020 and 2021. PV sales remained relatively resilient, as the chip shortage continued to ease and OEMs ramped up production. New Electric Vehicle sales increased by 182% YoY in February, despite the 30% reduction in the government subsidies for 2022, and the rising cost of batteries.
The Japanese market decelerated sharply in February, disrupted by skyrocketing Omicron infections and supply shortages of new vehicles. Rising inflation (in a country that is known for decades of deflationary trend) also dampened consumer confidence and spending. The February selling rate was 3.7 million units/year, down 21% from a robust January. In YoY terms, sales declined by 18% in February (the eighth consecutive month of contraction).
After a weak start to the New Year, sales in Korea accelerated in February. The February selling rate was 1.67 million units/year, up 10% from a weak January. The improvement in sales was expected, as a slump in January was caused mainly by the temporary shutdown of Hyundai’s Asan plant to upgrade the facility for production of the IONIQ 6 BEV. The easing of supply issues, including the chip shortage, also helped production and sales. In YoY terms, however, sales declined marginally due to a high-base effect.
Brazilian LV sales fell by 24.3% YoY in February, to 120,000 units. The selling rate increased to 1.75 million units/year in February, from 1.63 million units/year in January, but only in one month in 2021 was the selling rate lower than it was in February. In addition to supply-side issues, demand now appears to be waning as a result of declining affordability. A weak Real (BRL) is exacerbating inflation, and interest rates have been hiked sharply – and repeatedly – in an attempt to combat rising prices.
In Argentina, LV sales were down by 6.3% YoY in February, to 27,000 units. The selling rate increased to 350,000 units/year, up from 336,000 units/year in January. High inflation, rising interest rates (as required by an agreement with the International Monetary Fund), import restrictions, and chip-related inventory shortages are all contributing to the sluggish state of the market.
About Ken Zino
Ken Zino, editor and publisher of AutoInformed, is a versatile auto industry participant with global experience spanning decades in print and broadcast journalism, as well as social media. He has automobile testing, marketing, public relations and communications experience. He is past president of The International Motor Press Assn, the Detroit Press Club, founding member and first President of the Automotive Press Assn. He is a member of APA, IMPA and the Midwest Automotive Press Assn. He also brings an historical perspective while citing their contemporary relevance of the work of legendary auto writers such as Ken Purdy, Jim Dunne or Jerry Flint, or writers such as Red Smith, Mark Twain, Thomas Jefferson – all to bring perspective to a chaotic automotive universe. Above all, decades after he first drove a car, Zino still revels in the sound of the exhaust as the throttle is blipped during a downshift and the driver’s rush that occurs when the entry, apex and exit points of a turn are smoothly and swiftly crossed. It’s the beginning of a perfect lap. AutoInformed has an editorial philosophy that loves transportation machines of all kinds while promoting critical thinking about the future use of cars and trucks. Zino builds AutoInformed from his background in automotive journalism starting at Hearst Publishing in New York City on Motor and MotorTech Magazines and car testing where he reviewed hundreds of vehicles in his decade-long stint as the Detroit Bureau Chief of Road & Track magazine. Zino has also worked in Europe, and Asia – now the largest automotive market in the world with China at its center.