Tesla (Nasdaq: TSLA) is recalling 2,031,220 vehicles with Autopilot. Included are 2012-2023 Model S, 2016-2023 Model X, 2017-2023 Model 3 and 2020-2023 Model Y vehicles equipped with all versions of Autopilot with Autosteer leading up to the versions that contain the recall remedy, according to documents released by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration yesterday.
“In certain circumstances when Autosteer is engaged, the prominence and scope of the feature’s controls may not be sufficient to prevent driver misuse of the SAE Level 2 advanced driver-assistance feature,” Tesla said in the required NHTSA filing.
“There are too many drivers that are over-relying on the Tesla technology,” said Michael Brooks, Executive Director of the Center for Auto Safety.
Click to enlarge.
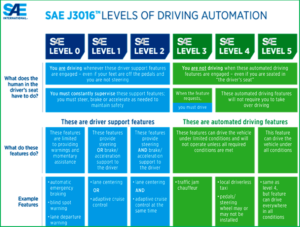
The full text version of the cause of the safety defect recall in the NHTSA filing said: “Basic Autopilot is a package that includes SAE Level 2 advanced driver- assistance features, including Autosteer and Traffic-Aware Cruise Control (TACC), that drivers may choose to engage subject to certain defined operating limitations. Autosteer is an SAE Level 2 advanced driver-assistance feature that, in coordination with the TACC feature, can provide steering, braking and acceleration support to the driver subject to certain limited operating conditions. Autosteer is designed and intended for use on controlled-access highways when the feature is not operating in conjunction with the Autosteer on City Streets feature. When Autosteer is engaged, as with all SAE Level 2 advanced driver-assistance features and systems, the driver is the operator of the vehicle. As the vehicle operator, the driver is responsible for the vehicle’s movement with their hands on the steering wheel at all times, remaining attentive to surrounding road conditions, and intervening (e.g., steer, brake, accelerate or apply the stalk) as needed to maintain safe operation.
“When Autosteer is engaged, it uses several controls to monitor that the driver is engaged in continuous and sustained responsibility for the vehicle’s operation as required. If the driver attempts to engage Autosteer when conditions are not met for engagement, the feature will alert the driver it is unavailable through visual and audible alerts, and Autosteer will not engage. Likewise, if the driver operates Autosteer in conditions where its functionality may be limited or has become deteriorated due to environmental or other circumstances, the feature may warn the driver with visual and audible alerts, restrict speed, and/or instruct the driver to intervene immediately.
“In certain circumstances when Autosteer is engaged, the prominence and scope of the feature’s controls may not be sufficient to prevent driver misuse of the SAE Level 2 advanced driver-assistance feature,” Tesla said in the NHTSA filing.
Chronology
- On 13 August 2021, NHTSA opened a Preliminary Evaluation (PE21-020) to investigate eleven incidents involving stationary first-responder vehicles and Tesla vehicles that were operating with Autosteer engaged. – Over the next year, as part of PE21-020, Tesla, in full cooperation, responded to extensive information requests from NHTSA and participated in several meetings with the agency.
- On 8 June 2022, NHTSA upgraded PE21-020 to Engineering Analysis (EA) EA22-002.
- Over the next year, as part of EA22-002, Tesla, in full cooperation, responded to extensive information requests from NHTSA and participated in several meetings with the agency.
- From 16 October 2023, through 4 December 2023, NHTSA and Tesla conducted several meetings to discuss the agency’s tentative conclusions regarding EA22-002, as they related to the issue of potential driver misuse when Autosteer is engaged, expectations to address the agency’s concerns through a voluntary recall, and Tesla’s proposed over-the-air (“OTA”) software remedies in response.
- While not concurring with the agency’s analysis, in the interest of resolving EA22-002, Tesla determined on 5 December 2023, to voluntarily administer a recall and provide the remedy below.
- As of 8 December 2023, Tesla has identified 9 warranty claims, received between 13 July 2021, and 17 September 2023, that may be related to this safety defect.
Remedy Program
- At no cost to customers as required by US regulations, affected vehicles will receive an over-the-air software remedy, which is expected to begin deploying to certain affected vehicles on or shortly after December 12, 2023 with software version 2023.44.30.
- Remaining affected vehicles will receive an over-the-air software remedy at a later date. The remedy will incorporate additional controls and alerts to those already existing on affected vehicles to further encourage the driver to adhere to their continuous driving responsibility whenever Autosteer is engaged, which includes keeping their hands on the steering wheel and paying attention to the roadway. Depending on vehicle hardware, the additional controls will include, among others, increasing the prominence of visual alerts on the user interface, simplifying engagement and disengagement of Autosteer, additional checks upon engaging Autosteer and while using the feature outside controlled access highways and when approaching traffic controls, and eventual suspension from Autosteer use if the driver repeatedly fails to demonstrate continuous and sustained driving responsibility while the feature is engaged.
- Tesla does not plan to include a statement in the Part 577 owner notification about pre-notice reimbursement because there are no out-of- warranty repairs related to this condition
- The remedy component incorporates the software remedy described above while the recalled component does not incorporate the software remedy described above.
- Beginning midday on December 7, 2023, Model S, Model X, Model 3 and Model Y vehicles in production received a software release that incorporates the software remedy.
- All Tesla stores and service centers will be notified about this recall on or shortly after December 12, 2023. Owner notification letters will be mailed 10 February 2024.

About Ken Zino
Ken Zino, editor and publisher of AutoInformed, is a versatile auto industry participant with global experience spanning decades in print and broadcast journalism, as well as social media. He has automobile testing, marketing, public relations and communications experience. He is past president of The International Motor Press Assn, the Detroit Press Club, founding member and first President of the Automotive Press Assn. He is a member of APA, IMPA and the Midwest Automotive Press Assn.
He also brings an historical perspective while citing their contemporary relevance of the work of legendary auto writers such as Ken Purdy, Jim Dunne or Jerry Flint, or writers such as Red Smith, Mark Twain, Thomas Jefferson – all to bring perspective to a chaotic automotive universe.
Above all, decades after he first drove a car, Zino still revels in the sound of the exhaust as the throttle is blipped during a downshift and the driver’s rush that occurs when the entry, apex and exit points of a turn are smoothly and swiftly crossed. It’s the beginning of a perfect lap.
AutoInformed has an editorial philosophy that loves transportation machines of all kinds while promoting critical thinking about the future use of cars and trucks.
Zino builds AutoInformed from his background in automotive journalism starting at Hearst Publishing in New York City on Motor and MotorTech Magazines and car testing where he reviewed hundreds of vehicles in his decade-long stint as the Detroit Bureau Chief of Road & Track magazine. Zino has also worked in Europe, and Asia – now the largest automotive market in the world with China at its center.


Tesla Recalls 2,031,220 Autopilot Equipped Vehicles
Tesla (Nasdaq: TSLA) is recalling 2,031,220 vehicles with Autopilot. Included are 2012-2023 Model S, 2016-2023 Model X, 2017-2023 Model 3 and 2020-2023 Model Y vehicles equipped with all versions of Autopilot with Autosteer leading up to the versions that contain the recall remedy, according to documents released by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration yesterday.
“In certain circumstances when Autosteer is engaged, the prominence and scope of the feature’s controls may not be sufficient to prevent driver misuse of the SAE Level 2 advanced driver-assistance feature,” Tesla said in the required NHTSA filing.
“There are too many drivers that are over-relying on the Tesla technology,” said Michael Brooks, Executive Director of the Center for Auto Safety.
Click to enlarge.
The full text version of the cause of the safety defect recall in the NHTSA filing said: “Basic Autopilot is a package that includes SAE Level 2 advanced driver- assistance features, including Autosteer and Traffic-Aware Cruise Control (TACC), that drivers may choose to engage subject to certain defined operating limitations. Autosteer is an SAE Level 2 advanced driver-assistance feature that, in coordination with the TACC feature, can provide steering, braking and acceleration support to the driver subject to certain limited operating conditions. Autosteer is designed and intended for use on controlled-access highways when the feature is not operating in conjunction with the Autosteer on City Streets feature. When Autosteer is engaged, as with all SAE Level 2 advanced driver-assistance features and systems, the driver is the operator of the vehicle. As the vehicle operator, the driver is responsible for the vehicle’s movement with their hands on the steering wheel at all times, remaining attentive to surrounding road conditions, and intervening (e.g., steer, brake, accelerate or apply the stalk) as needed to maintain safe operation.
“When Autosteer is engaged, it uses several controls to monitor that the driver is engaged in continuous and sustained responsibility for the vehicle’s operation as required. If the driver attempts to engage Autosteer when conditions are not met for engagement, the feature will alert the driver it is unavailable through visual and audible alerts, and Autosteer will not engage. Likewise, if the driver operates Autosteer in conditions where its functionality may be limited or has become deteriorated due to environmental or other circumstances, the feature may warn the driver with visual and audible alerts, restrict speed, and/or instruct the driver to intervene immediately.
“In certain circumstances when Autosteer is engaged, the prominence and scope of the feature’s controls may not be sufficient to prevent driver misuse of the SAE Level 2 advanced driver-assistance feature,” Tesla said in the NHTSA filing.
Chronology
Remedy Program
About Ken Zino
Ken Zino, editor and publisher of AutoInformed, is a versatile auto industry participant with global experience spanning decades in print and broadcast journalism, as well as social media. He has automobile testing, marketing, public relations and communications experience. He is past president of The International Motor Press Assn, the Detroit Press Club, founding member and first President of the Automotive Press Assn. He is a member of APA, IMPA and the Midwest Automotive Press Assn. He also brings an historical perspective while citing their contemporary relevance of the work of legendary auto writers such as Ken Purdy, Jim Dunne or Jerry Flint, or writers such as Red Smith, Mark Twain, Thomas Jefferson – all to bring perspective to a chaotic automotive universe. Above all, decades after he first drove a car, Zino still revels in the sound of the exhaust as the throttle is blipped during a downshift and the driver’s rush that occurs when the entry, apex and exit points of a turn are smoothly and swiftly crossed. It’s the beginning of a perfect lap. AutoInformed has an editorial philosophy that loves transportation machines of all kinds while promoting critical thinking about the future use of cars and trucks. Zino builds AutoInformed from his background in automotive journalism starting at Hearst Publishing in New York City on Motor and MotorTech Magazines and car testing where he reviewed hundreds of vehicles in his decade-long stint as the Detroit Bureau Chief of Road & Track magazine. Zino has also worked in Europe, and Asia – now the largest automotive market in the world with China at its center.