Click to enlarge.
Stellantis (NYSE: STLA) claims it has created the world’s first virtual cockpit platform as part of its Stellantis Virtual Engineering Workbench (VEW). This will allow the delivery of infotainment tech to customers 100 times faster than previous processes, it’s said. The new platform uses the QNX® Hypervisor in the cloud from BlackBerry, which is now on early access release via AWS Marketplace within the QNX Accelerate portfolio of cloud-based tools.
“Software is becoming increasingly crucial in vehicles, leading us to innovate in how we develop and validate it,” said Yves Bonnefont, chief software officer at Stellantis. “With our virtual cockpit, we’re revolutionizing not just our approach, but also that of our suppliers and partners in the industry. Essentially, we’re able to get closer to our customer’s needs through this technology with faster development cycles, faster feedback loops, and quicker delivery of the technology they use and love. It’s a leap toward customer-first innovation and efficiency in the automotive world.”
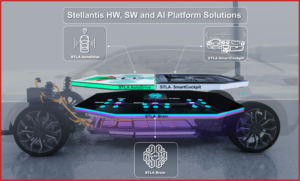
Software is a key building block for Stellantis to design, develop, test, manufacture and sell clean, safe and affordable mobility, as outlined in the Dare Forward 2030 strategic plan. It is the driving force behind the AI-powered STLA Brain, STLA SmartCockpit and STLA AutoDrive technology platforms. In 2022, Stellantis selected AWS as its preferred cloud provider for vehicle platforms and the companies began work on the Stellantis’ purpose-built, in-house VEW.
Accessing QNX Hypervisor via AWS Marketplace enables Stellantis to include a virtual cockpit high-performance computing (HPC) simulation into a cloud environment. This industry-first platform for mixed-criticality and multi-OS embedded application development includes QNX Hypervisor Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) and industry-standard hardware interfaces as defined in the VirtIO standard Trout v1.2. With tools such as virtualization of graphics, audio and touchscreen/mouse/keyboard inputs, the development method offers little to no difference between running QNX Hypervisor-based systems in the cloud versus on real hardware, according to Stellantis.
Taking a software-driven approach and deploying the QNX Hypervisor in the cloud, Stellantis says it can accelerate customer feedback sessions, and with minimal effort, replicate the cockpit experience of a particular brand and vehicle, and make changes in real time to optimize the experience for the driver. This real-time feedback, underpinned by low-latency access to the cloud, allows Stellantis to solicit valuable feedback from its customer and developer base to build future infotainment features and applications.
The proof of all these claims awaits customer sales and satisfaction.
AutoInformed on

About Ken Zino
Ken Zino, editor and publisher of AutoInformed, is a versatile auto industry participant with global experience spanning decades in print and broadcast journalism, as well as social media. He has automobile testing, marketing, public relations and communications experience. He is past president of The International Motor Press Assn, the Detroit Press Club, founding member and first President of the Automotive Press Assn. He is a member of APA, IMPA and the Midwest Automotive Press Assn.
He also brings an historical perspective while citing their contemporary relevance of the work of legendary auto writers such as Ken Purdy, Jim Dunne or Jerry Flint, or writers such as Red Smith, Mark Twain, Thomas Jefferson – all to bring perspective to a chaotic automotive universe.
Above all, decades after he first drove a car, Zino still revels in the sound of the exhaust as the throttle is blipped during a downshift and the driver’s rush that occurs when the entry, apex and exit points of a turn are smoothly and swiftly crossed. It’s the beginning of a perfect lap.
AutoInformed has an editorial philosophy that loves transportation machines of all kinds while promoting critical thinking about the future use of cars and trucks.
Zino builds AutoInformed from his background in automotive journalism starting at Hearst Publishing in New York City on Motor and MotorTech Magazines and car testing where he reviewed hundreds of vehicles in his decade-long stint as the Detroit Bureau Chief of Road & Track magazine. Zino has also worked in Europe, and Asia – now the largest automotive market in the world with China at its center.


Stellantis, BlackBerry QNX and AWS Launch Virtual Cockpit
Click to enlarge.
Stellantis (NYSE: STLA) claims it has created the world’s first virtual cockpit platform as part of its Stellantis Virtual Engineering Workbench (VEW). This will allow the delivery of infotainment tech to customers 100 times faster than previous processes, it’s said. The new platform uses the QNX® Hypervisor in the cloud from BlackBerry, which is now on early access release via AWS Marketplace within the QNX Accelerate portfolio of cloud-based tools.
“Software is becoming increasingly crucial in vehicles, leading us to innovate in how we develop and validate it,” said Yves Bonnefont, chief software officer at Stellantis. “With our virtual cockpit, we’re revolutionizing not just our approach, but also that of our suppliers and partners in the industry. Essentially, we’re able to get closer to our customer’s needs through this technology with faster development cycles, faster feedback loops, and quicker delivery of the technology they use and love. It’s a leap toward customer-first innovation and efficiency in the automotive world.”
Software is a key building block for Stellantis to design, develop, test, manufacture and sell clean, safe and affordable mobility, as outlined in the Dare Forward 2030 strategic plan. It is the driving force behind the AI-powered STLA Brain, STLA SmartCockpit and STLA AutoDrive technology platforms. In 2022, Stellantis selected AWS as its preferred cloud provider for vehicle platforms and the companies began work on the Stellantis’ purpose-built, in-house VEW.
Accessing QNX Hypervisor via AWS Marketplace enables Stellantis to include a virtual cockpit high-performance computing (HPC) simulation into a cloud environment. This industry-first platform for mixed-criticality and multi-OS embedded application development includes QNX Hypervisor Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) and industry-standard hardware interfaces as defined in the VirtIO standard Trout v1.2. With tools such as virtualization of graphics, audio and touchscreen/mouse/keyboard inputs, the development method offers little to no difference between running QNX Hypervisor-based systems in the cloud versus on real hardware, according to Stellantis.
Taking a software-driven approach and deploying the QNX Hypervisor in the cloud, Stellantis says it can accelerate customer feedback sessions, and with minimal effort, replicate the cockpit experience of a particular brand and vehicle, and make changes in real time to optimize the experience for the driver. This real-time feedback, underpinned by low-latency access to the cloud, allows Stellantis to solicit valuable feedback from its customer and developer base to build future infotainment features and applications.
The proof of all these claims awaits customer sales and satisfaction.
AutoInformed on
About Ken Zino
Ken Zino, editor and publisher of AutoInformed, is a versatile auto industry participant with global experience spanning decades in print and broadcast journalism, as well as social media. He has automobile testing, marketing, public relations and communications experience. He is past president of The International Motor Press Assn, the Detroit Press Club, founding member and first President of the Automotive Press Assn. He is a member of APA, IMPA and the Midwest Automotive Press Assn. He also brings an historical perspective while citing their contemporary relevance of the work of legendary auto writers such as Ken Purdy, Jim Dunne or Jerry Flint, or writers such as Red Smith, Mark Twain, Thomas Jefferson – all to bring perspective to a chaotic automotive universe. Above all, decades after he first drove a car, Zino still revels in the sound of the exhaust as the throttle is blipped during a downshift and the driver’s rush that occurs when the entry, apex and exit points of a turn are smoothly and swiftly crossed. It’s the beginning of a perfect lap. AutoInformed has an editorial philosophy that loves transportation machines of all kinds while promoting critical thinking about the future use of cars and trucks. Zino builds AutoInformed from his background in automotive journalism starting at Hearst Publishing in New York City on Motor and MotorTech Magazines and car testing where he reviewed hundreds of vehicles in his decade-long stint as the Detroit Bureau Chief of Road & Track magazine. Zino has also worked in Europe, and Asia – now the largest automotive market in the world with China at its center.