Hyundai Motor said today it intends to leverage its expertise to bolster its position in the hybrid market under its new Hyundai Dynamic Capabilities strategy, a flexible response to the EV market based on core capabilities. Executive summary – Hyundai is modifying its EV strategy in the face of weak EV demand. Under this change in ways, Hyundai will expand the application of its hybrid system beyond compact and mid-size cars to small, large and luxury vehicles. This will increase its current range from seven to 14 models. This expansion will encompass not only Hyundai vehicles but also its luxury brand, Genesis, which will offer a hybrid option for all models, excluding those that are exclusively electric.
“In the electrification era, Hyundai has distinguished itself by rapidly launching a comprehensive lineup of EVs, catering not only to mass-market brands but also to the luxury and high-performance segments,” said Jaehoon Chang, President and CEO of Hyundai Motor Company. “Building on our advanced technology and dedication to innovation, we aim to secure a leading position in the market as the adoption of electrified vehicles gains momentum.”
Click to enlarge.
By 2028, Hyundai wants to sell 1.33 million electrified units, an increase of over 40% of its global sales plan from the previous 2027 year. The company anticipates a surge in hybrid demand, particularly in North America, where it plans to increase its hybrid vehicle volume to 690,000 units by 2030. It will adjust its hybrid sales expansion to meet the demand in each region, including Korea and Europe.
To facilitate this ambitious plan, Hyundai Motor claimed it has secured a versatile production system and parts supply network, making full use of its major global factories and introducing hybrid models, resulting in what’s said [hoped?] cost reduction and profitability enhancement. It plans to manufacture hybrid vehicles at the Hyundai Motor Group Metaplant America (HMGMA) in Georgia alongside its dedicated EV models, including IONIQ 5 and IONIQ 9, a planned three-row fully electric SUV. This strategy it’s said will allow the company to respond swiftly to the North American market, which currently faces a shortage of hybrid supply, and to increase the operational efficiency of the factory.
The company will also introduce the next-generation TMED-II system. This enhanced version of its existing hybrid system has achieved what’s claimed to be the world’s highest level of competitiveness by significantly improving performance and fuel efficiency compared to the existing system. This system is slated for integration into production vehicles starting from January 2025. Future hybrid vehicles will be equipped with premium technologies such as smart regenerative braking and V2L bi-directional charging, enhancing product value and cementing Hyundai Motor’s standing in the market with superior product quality.
Hyundai Motor is also developing a new EREV (extended range EV – a plug-in hybrid with a small battery and a gasoline engine) under its Hyundai Dynamic Capabilities strategy. The new EREV will combine the advantages of internal combustion engines (ICE) and EVs. Hyundai Motor has developed a unique new powertrain and power electronics (PT/PE) system to enable four-wheel drive with the application of two motors. The operation is powered solely by electricity, similar to EVs, with the engine being used only for battery charging.
Hyundai plans to begin mass production of the new EREV in North America and China by the end of 2026, with strong sales commencing in 2027. In the North American market, the company will initially launch D-class SUV models of Hyundai and Genesis brands to meet the remaining demand for internal combustion engines, with a target of 80,000-plus units.
In China, where price competitiveness is crucial, Hyundai Motor plans to respond using an economical C-segment platform, with a target of 30,000-plus units. The company will also review further expansion plans in line with future market conditions.
The company aims to address the EV deceleration by expanding its hybrid and new EREV offerings and gradually increasing EV models by 2030 when a recovery in EV demand is expected. Hyundai Motor aims to build a full lineup of EVs, from affordable EVs to luxury and high-performance models, and launch 21 models by 2030 to provide consumers with various options. Hyundai Motor plans to expedite the development of next-generation batteries, including solid-state batteries. The company is set to continue development in its next-generation battery research building, which is scheduled to open at Hyundai Motor’s Uiwang Research Institute later this year. This initiative is aimed at reinforcing the company’s leadership in next-generation battery technology.
The company also plans to apply the battery CTV (cell-to-vehicle) structure optimized for the company. In the CTV structure, by integrating the battery and the vehicle body, the company can improve battery integration and performance, reduce parts to lighten the weight by 10% compared to the previous CTP (cell-to-pack) system.
By 2030, Hyundai Motor aims to not only use current performance-based NCM (nickel-cobalt-manganese) batteries and low-cost LFP (lithium-iron-phosphate) batteries but also develop a new, affordable NCM battery. This new entry-level battery will first be implemented in volume models, with the company anticipating a battery performance enhancement of over 20% by 2030, through ongoing improvements in battery energy density.
In the second part of the Hyundai Way, the Mobility Game Changer strategy outlines Hyundai Motor’s software (SW)-centric transition strategy. The company is continuously enhancing its products and services based on SW and AI. It focuses on the development of Software-Defined Vehicles (SDVs), including an SDV Pace Car, and new mobility businesses, leading the transformation in the mobility ecosystem.
Hyundai Motor is transitioning to a development system for SDVs by incorporating software development methods into vehicle development. The core of SDV development includes the creation of hardware devices that can collect a variety of data from inside and outside the vehicle, and the ability to control the overall vehicle interface based on software. The company aims to connect SDV devices with fleets, logistics and urban transportation infrastructure, building a data infrastructure that can generate, collect, and utilize large amounts of data in various fields.
Utilizing AI and digital twin technology, Hyundai Motor will efficiently manage the real-time operation status of various mobilities and traffic conditions. The company will continuously enhance cybersecurity technology to develop safer and more reliable connected services.
Furthermore, by offering a third-party software developer kit (SDK) and app market, numerous IT developers and mobility service providers will be able to develop various services using Hyundai Motor’s data infrastructure. This will contribute to the creation of the SDV future mobility ecosystem, based on 42dot’s SW technology platform.
Hyundai Motor is developing a Zonal Electric-Electronic (E/E) architecture based on a high-performance vehicle computer (HPVC) for optimized SDV devices in terms of power, control and communication. The application of such an architecture can simplify the existing complex vehicle structure, reducing development time and cost, and increasing the flexibility of software changes, enabling faster improvement and deployment of services and functions.
Financial Aspects of Changed Hyundai Way
Hyundai Motor’s CFO, Seung Jo Lee, outlined the company’s financial strategies. He announced Hyundai Motor’s mid- to long-term investment plan, profitability target, value-up program, and subsequent shareholder return policy, all crucial elements in successfully executing the ‘Hyundai Way’ strategy.
Forthcoming 10-year Investment Plan
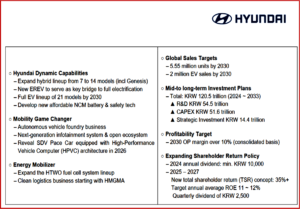
- Hyundai Motor has a new total investment of KRW 120.5 trillion for the next decade, from 2024 to 2033. This is KRW 11.1 trillion more than what was announced last year.
- The investment breakdown includes KRW 54.5 trillion for Research and Development (R&D).
- KRW 51.6 trillion for Capital Expenditure (CAPEX).
- KRW 14.4 trillion for strategic investments.
In alignment with the Hyundai Way strategy, which encompasses Hyundai Dynamic Capabilities, Mobility Game Changer and Energy Mobilizer, the company emphasized its investment plan will be implemented in phases.
- Under the Hyundai Dynamic Capabilities strategy, the company plans to invest a total of KRW 92.7 trillion. This includes KRW 37.4 trillion for Research and Development (R&D), KRW 50.8 trillion for Capital Expenditure (CAPEX), and KRW 4.5 trillion for strategic investments. This investment aims to bolster Hyundai’s competitiveness in the era of electrification, focusing on hybrids, new EREVs, next-generation modular architecture and battery technologies.
- Under the Mobility Game Changer strategy, Hyundai Motor plans to invest KRW 22.1 trillion in advanced software and E/E architecture, leveraging its expertise in hardware development and production. This investment is also intended to bolster the company’s future pursuits in autonomous driving, software-defined vehicles, and robotics.
- Under the Energy Mobilizer strategy, Hyundai Motor plans to invest KRW 5.7 trillion to develop hydrogen ecosystems and value chains, further enhancing its existing expertise in hydrogen energy.
Mid- to Long-term Financial Goals
- Hyundai Motor targets an operating profit margin of 9% – 10% in 2027 and more than 10 % in 2030 through continuous cost enhancements for EVs and the introduction of EREV models.
- The company expects to achieve equal profitability on its entire powertrain lineup, including ICE, hybrids, EREVs and EVs by 2030.
Shareholder Return Policy is a new total shareholder return (TSR) concept. This includes dividends, as well as the cancellation and buyback of treasury stocks.
- Starting in 2024, Hyundai Motor has committed to paying a minimum annual dividend of KRW 10,000 to its shareholders. The company also plans to transparently communicate its rationale for share buyback, by either enhancing Hyundai Motor’s corporate value or distributing the stocks to its employees.
- From 2025 to 2027, Hyundai Motor will employ a proactive and sustainable TSR of more than 35%. This will involve a flexible approach between the sum of dividends, buybacks and cancellations of treasury stocks. During this period, the company aims to achieve an average ROE of 11 -12 %.
- Over the next three years, Hyundai Motor will initiate a stock buyback program worth up to a total of KRW 4 trillion, in accordance with the TSR. The annual amount will be flexibly determined based on the company’s return on equity (ROE) targets.
- Hyundai will offer a minimum quarterly dividend of KRW 2500, representing an increase of 25% compared to the current year. In instances of retiring or repurchasing treasury shares, the company will also consider the value of its preferred stocks.


EV Grumblings – Hyundai Motor Changes Its Way
Hyundai Motor said today it intends to leverage its expertise to bolster its position in the hybrid market under its new Hyundai Dynamic Capabilities strategy, a flexible response to the EV market based on core capabilities. Executive summary – Hyundai is modifying its EV strategy in the face of weak EV demand. Under this change in ways, Hyundai will expand the application of its hybrid system beyond compact and mid-size cars to small, large and luxury vehicles. This will increase its current range from seven to 14 models. This expansion will encompass not only Hyundai vehicles but also its luxury brand, Genesis, which will offer a hybrid option for all models, excluding those that are exclusively electric.
“In the electrification era, Hyundai has distinguished itself by rapidly launching a comprehensive lineup of EVs, catering not only to mass-market brands but also to the luxury and high-performance segments,” said Jaehoon Chang, President and CEO of Hyundai Motor Company. “Building on our advanced technology and dedication to innovation, we aim to secure a leading position in the market as the adoption of electrified vehicles gains momentum.”
Click to enlarge.
By 2028, Hyundai wants to sell 1.33 million electrified units, an increase of over 40% of its global sales plan from the previous 2027 year. The company anticipates a surge in hybrid demand, particularly in North America, where it plans to increase its hybrid vehicle volume to 690,000 units by 2030. It will adjust its hybrid sales expansion to meet the demand in each region, including Korea and Europe.
To facilitate this ambitious plan, Hyundai Motor claimed it has secured a versatile production system and parts supply network, making full use of its major global factories and introducing hybrid models, resulting in what’s said [hoped?] cost reduction and profitability enhancement. It plans to manufacture hybrid vehicles at the Hyundai Motor Group Metaplant America (HMGMA) in Georgia alongside its dedicated EV models, including IONIQ 5 and IONIQ 9, a planned three-row fully electric SUV. This strategy it’s said will allow the company to respond swiftly to the North American market, which currently faces a shortage of hybrid supply, and to increase the operational efficiency of the factory.
The company will also introduce the next-generation TMED-II system. This enhanced version of its existing hybrid system has achieved what’s claimed to be the world’s highest level of competitiveness by significantly improving performance and fuel efficiency compared to the existing system. This system is slated for integration into production vehicles starting from January 2025. Future hybrid vehicles will be equipped with premium technologies such as smart regenerative braking and V2L bi-directional charging, enhancing product value and cementing Hyundai Motor’s standing in the market with superior product quality.
Hyundai Motor is also developing a new EREV (extended range EV – a plug-in hybrid with a small battery and a gasoline engine) under its Hyundai Dynamic Capabilities strategy. The new EREV will combine the advantages of internal combustion engines (ICE) and EVs. Hyundai Motor has developed a unique new powertrain and power electronics (PT/PE) system to enable four-wheel drive with the application of two motors. The operation is powered solely by electricity, similar to EVs, with the engine being used only for battery charging.
Hyundai plans to begin mass production of the new EREV in North America and China by the end of 2026, with strong sales commencing in 2027. In the North American market, the company will initially launch D-class SUV models of Hyundai and Genesis brands to meet the remaining demand for internal combustion engines, with a target of 80,000-plus units.
In China, where price competitiveness is crucial, Hyundai Motor plans to respond using an economical C-segment platform, with a target of 30,000-plus units. The company will also review further expansion plans in line with future market conditions.
The company aims to address the EV deceleration by expanding its hybrid and new EREV offerings and gradually increasing EV models by 2030 when a recovery in EV demand is expected. Hyundai Motor aims to build a full lineup of EVs, from affordable EVs to luxury and high-performance models, and launch 21 models by 2030 to provide consumers with various options. Hyundai Motor plans to expedite the development of next-generation batteries, including solid-state batteries. The company is set to continue development in its next-generation battery research building, which is scheduled to open at Hyundai Motor’s Uiwang Research Institute later this year. This initiative is aimed at reinforcing the company’s leadership in next-generation battery technology.
The company also plans to apply the battery CTV (cell-to-vehicle) structure optimized for the company. In the CTV structure, by integrating the battery and the vehicle body, the company can improve battery integration and performance, reduce parts to lighten the weight by 10% compared to the previous CTP (cell-to-pack) system.
By 2030, Hyundai Motor aims to not only use current performance-based NCM (nickel-cobalt-manganese) batteries and low-cost LFP (lithium-iron-phosphate) batteries but also develop a new, affordable NCM battery. This new entry-level battery will first be implemented in volume models, with the company anticipating a battery performance enhancement of over 20% by 2030, through ongoing improvements in battery energy density.
In the second part of the Hyundai Way, the Mobility Game Changer strategy outlines Hyundai Motor’s software (SW)-centric transition strategy. The company is continuously enhancing its products and services based on SW and AI. It focuses on the development of Software-Defined Vehicles (SDVs), including an SDV Pace Car, and new mobility businesses, leading the transformation in the mobility ecosystem.
Hyundai Motor is transitioning to a development system for SDVs by incorporating software development methods into vehicle development. The core of SDV development includes the creation of hardware devices that can collect a variety of data from inside and outside the vehicle, and the ability to control the overall vehicle interface based on software. The company aims to connect SDV devices with fleets, logistics and urban transportation infrastructure, building a data infrastructure that can generate, collect, and utilize large amounts of data in various fields.
Utilizing AI and digital twin technology, Hyundai Motor will efficiently manage the real-time operation status of various mobilities and traffic conditions. The company will continuously enhance cybersecurity technology to develop safer and more reliable connected services.
Furthermore, by offering a third-party software developer kit (SDK) and app market, numerous IT developers and mobility service providers will be able to develop various services using Hyundai Motor’s data infrastructure. This will contribute to the creation of the SDV future mobility ecosystem, based on 42dot’s SW technology platform.
Hyundai Motor is developing a Zonal Electric-Electronic (E/E) architecture based on a high-performance vehicle computer (HPVC) for optimized SDV devices in terms of power, control and communication. The application of such an architecture can simplify the existing complex vehicle structure, reducing development time and cost, and increasing the flexibility of software changes, enabling faster improvement and deployment of services and functions.
Financial Aspects of Changed Hyundai Way
Hyundai Motor’s CFO, Seung Jo Lee, outlined the company’s financial strategies. He announced Hyundai Motor’s mid- to long-term investment plan, profitability target, value-up program, and subsequent shareholder return policy, all crucial elements in successfully executing the ‘Hyundai Way’ strategy.
Forthcoming 10-year Investment Plan
In alignment with the Hyundai Way strategy, which encompasses Hyundai Dynamic Capabilities, Mobility Game Changer and Energy Mobilizer, the company emphasized its investment plan will be implemented in phases.
Mid- to Long-term Financial Goals
Shareholder Return Policy is a new total shareholder return (TSR) concept. This includes dividends, as well as the cancellation and buyback of treasury stocks.
About Ken Zino
Ken Zino, editor and publisher of AutoInformed, is a versatile auto industry participant with global experience spanning decades in print and broadcast journalism, as well as social media. He has automobile testing, marketing, public relations and communications experience. He is past president of The International Motor Press Assn, the Detroit Press Club, founding member and first President of the Automotive Press Assn. He is a member of APA, IMPA and the Midwest Automotive Press Assn. He also brings an historical perspective while citing their contemporary relevance of the work of legendary auto writers such as Ken Purdy, Jim Dunne or Jerry Flint, or writers such as Red Smith, Mark Twain, Thomas Jefferson – all to bring perspective to a chaotic automotive universe. Above all, decades after he first drove a car, Zino still revels in the sound of the exhaust as the throttle is blipped during a downshift and the driver’s rush that occurs when the entry, apex and exit points of a turn are smoothly and swiftly crossed. It’s the beginning of a perfect lap. AutoInformed has an editorial philosophy that loves transportation machines of all kinds while promoting critical thinking about the future use of cars and trucks. Zino builds AutoInformed from his background in automotive journalism starting at Hearst Publishing in New York City on Motor and MotorTech Magazines and car testing where he reviewed hundreds of vehicles in his decade-long stint as the Detroit Bureau Chief of Road & Track magazine. Zino has also worked in Europe, and Asia – now the largest automotive market in the world with China at its center.